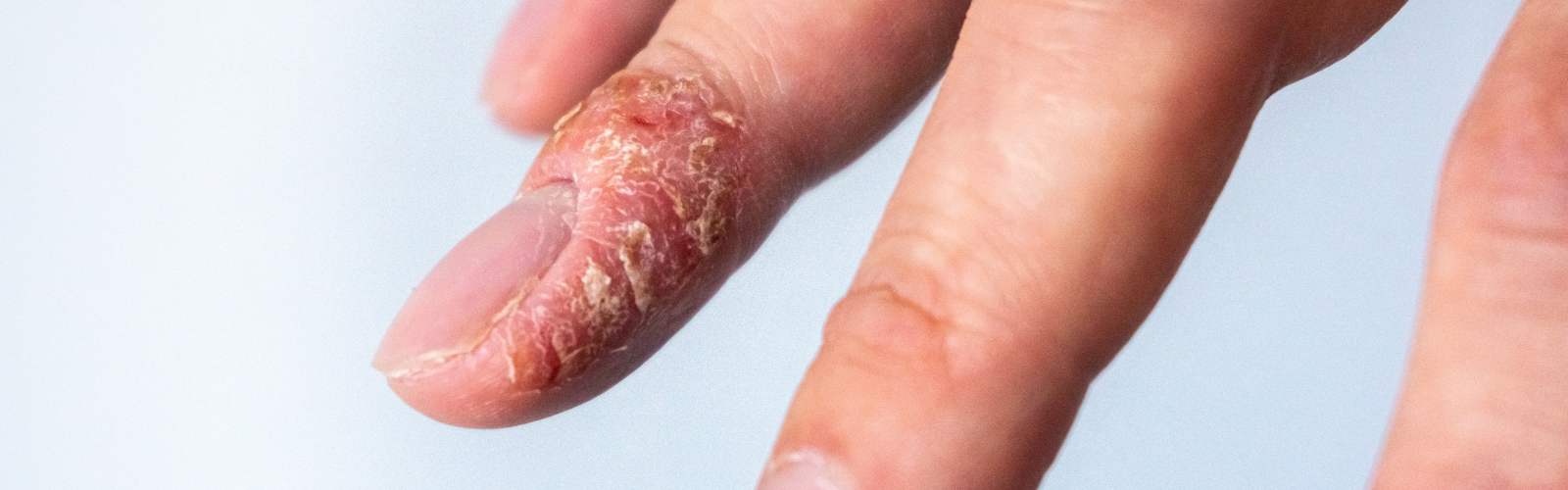
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a medical condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation on the skin. There are several types of dermatitis, but the most common include contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis (eczema), and seborrheic dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes in contact with an irritant or allergen. Common irritants include detergents, soaps, perfumes, and cleaning products. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a chronic condition where the skin becomes inflamed, itchy, and red most commonly due to a genetic predisposition and mutation in one of the genes that hold the skin cells together called fillagrin. Seborrheic dermatitis is the inflammation of the skin that typically occurs on oily areas of the body, such as the scalp and face, and is often characterized by scaly skin and dandruff.
What to Expect
The treatment for dermatitis depends on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
Topical creams and ointments: These are applied directly to the affected area and can include corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immune-suppressing drugs to manage inflammation and itching.
Moisturizers: Frequently moisturizing dry or scaly skin can help prevent flare-ups and reduce itchiness.
Wet dressings or wet wraps: This method involves applying a cool and wet compress made of medicated and non-medicated materials to reduce and soothe inflamed skin.
Identifying and avoiding triggers: Identifying the triggers that cause dermatitis outbreaks is important in managing and preventing future incidences. This could include avoiding certain types of fabrics, allergens or irritants, or changing diet.
Phototherapy: UV light therapy can help manage certain types of dermatitis. UVB light can slow the production of skin cells, which in turn reduces the inflammation and itching.
Medications: In severe cases of dermatitis, systemic medications such as oral corticosteroids or immunomodulators such as dupilumab or JAK inhibitors may also be prescribed by Dr. Lenzy.
It's essential to consult a board-certified dermatologist or qualified dermatological provider to get a proper diagnosis and the right treatment plan for dermatitis.

